With the development of electronic design toward thin and light, the high density integration (HDI) technology in PCB manufacturing process makes the end product design more miniaturized, while meeting the requirements of electronic performance and efficiency. HDI is widely used in mobile phone, digital, automotive electronics and other products. Cracks at the bottom of HDI blind holes and other anomalies are one of the reliability problems of high density interconnect PRINTED circuit boards, which are difficult to be detected in the manufacturing process due to multiple factors. The industry calls them typical gray defects, which are often found after the quality problems occur in the terminal installation, resulting in large claims.
The hot and cold shock test chamber can be used to test the reliability and failure analysis of coatings on HDI and double-sided multilayer boards. Our hot and cold impact test chamber can provide the most severe test conditions, the impact temperature range is -65℃~+150℃, continuous operation more than 1000 cycles without defrosting, no need to provide compressed air, provide a variety of working mode options, low energy consumption, while providing high performance testing for the laboratory energy saving and cost control to provide the best solution.
Specific cases are as follows:
Our client, a laboratory in Guangdong, conducts coating reliability and failure analysis for HDI and double-sided multilayer boards. The laboratory has the following test methods for "coating reliability analysis" : hot and cold shock, reflow welding test, mechanical grinding, argon ion polishing, FIB ion beam sample preparation, and scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy analysis.

Case 1: For PCB board cold and hot shock test and detection of resistance change, coating reliability can be observed through argon ion polishing or FIB cutting to observe the cracks between coatings, coating open circuit, hole wall separation and other defects, to specify the direction for PCB board factory process selection.
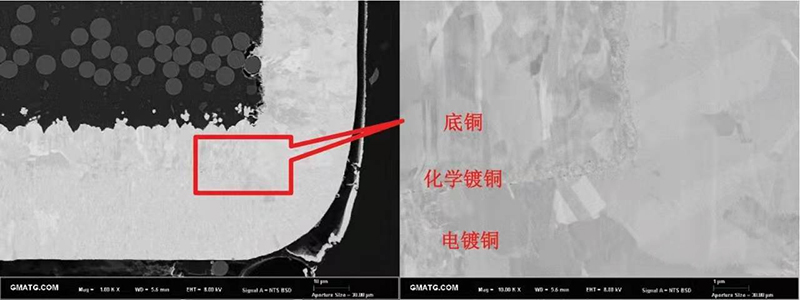
Case 2: After argon ion polishing, the morphology of different coatings can be observed by field emission electron microscope, which can intuitively determine whether there is columnar crystallization and other crystal states that seriously affect the thermal reliability of the coatings. It can also observe whether there are "holes", "cracks" and other anomalies that are not easy to monitor between different coatings.